Anatomy Of Face

Facial Muscles JOI Jacksonville Orthopaedic Institute
Head shape and upper face shape are closely related to the shape of the bony skull. Figures 1 and 2 show the bony anatomy of the face. Many anthropological landmarks, bony and soft tissue, are illustrated in Figures 3 and 4. Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Figure 4. The anatomy of the various structures is described in more detail below. Cranium:
FACE Anatomy muscle veins Detailed EDUCATIONAL SCIENCE poster Etsy
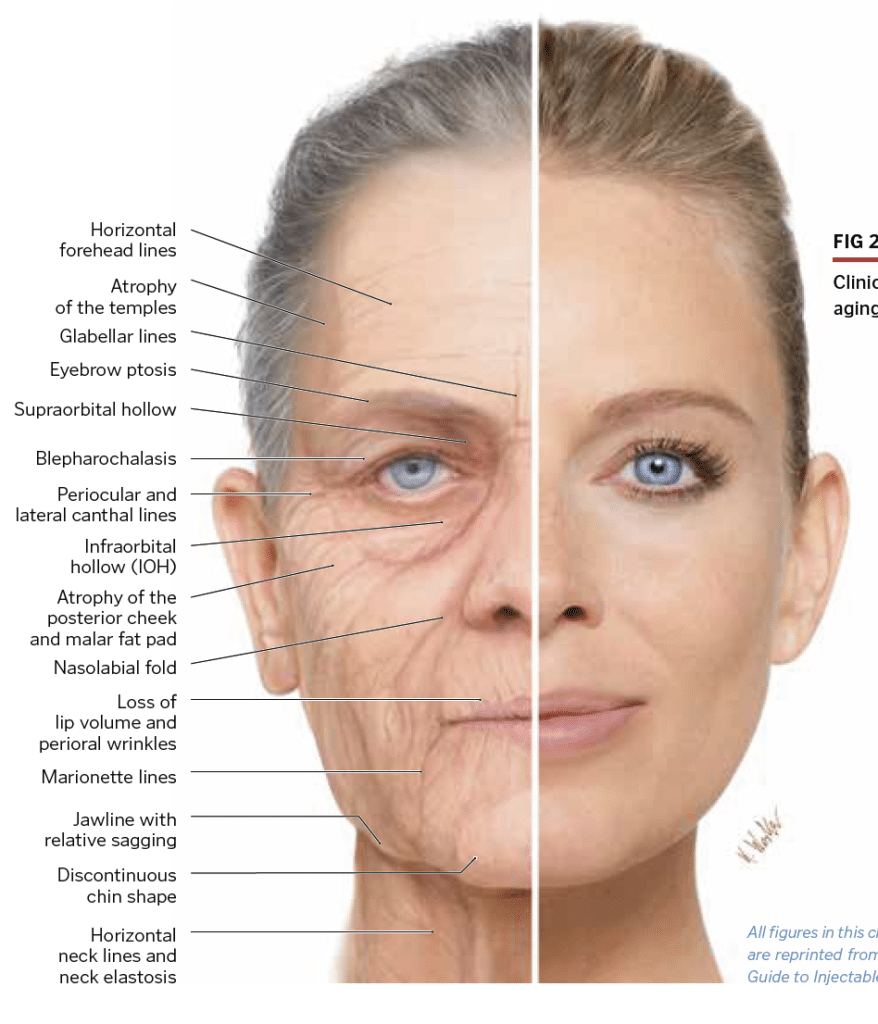
1.10.1 Aging Process of the Facial Tissue. The anatomical structures of the face related to aging comprise of the facial bone, fat tissue, fibrous connective tissue, and facial muscles. The bony tissue is a structure that forms the basic frame of the face and bone remodeling goes throughout lifelong period.

Face_anatomy_muscle_veins_detailed_educational_science_poster1 Etsy Face anatomy, Facial
Skeletal anatomy of the face The face is the feature which best distinguishes a person. Specialized regions of the human brain, such as the fusiform face area (FFA), enable facial recognition; when these are damaged, it may be impossible to recognize faces even of intimate family members.
Face Diagram Visual Diagram
The surface anatomy of the face, although highly variable in appearance, has several constant landmarks illustrated in this figure. Full size image. Muscles of Facial Expression. The muscles of facial expression are located in the subcutaneous tissue. They attach to fascia or bone and insert into the skin. When they contract, they produce the.

Facial Anatomy Considerations for Aesthetic Providers by KevinCease 2D CGSociety
The curved part of a bone that gives structural support to the rest of the bone. Above: Markings of the facial bones with the following views: (A) anterior view, (B) lateral view of the left side of the skull, (C) inferior view with the mandible removed, and (D) lateral view of the right side of the skull. Marking.

Face anatomy by JosueVilela Medical Visualization Sculpture CGSociety
Anatomy of the Facial Skeleton The facial skeleton or viscerocranium is formed by the 14 bones mentioned above. Except for the mandible, these bones are joined by sutures via synarthrodial or immovable joints. Here is a basic outline for the bones of the face: 1. Zygomatic: Located at the cheek region below the eye sockets on either side.
Basics to Facial Esthetics Facial anatomy CARE Esthetics
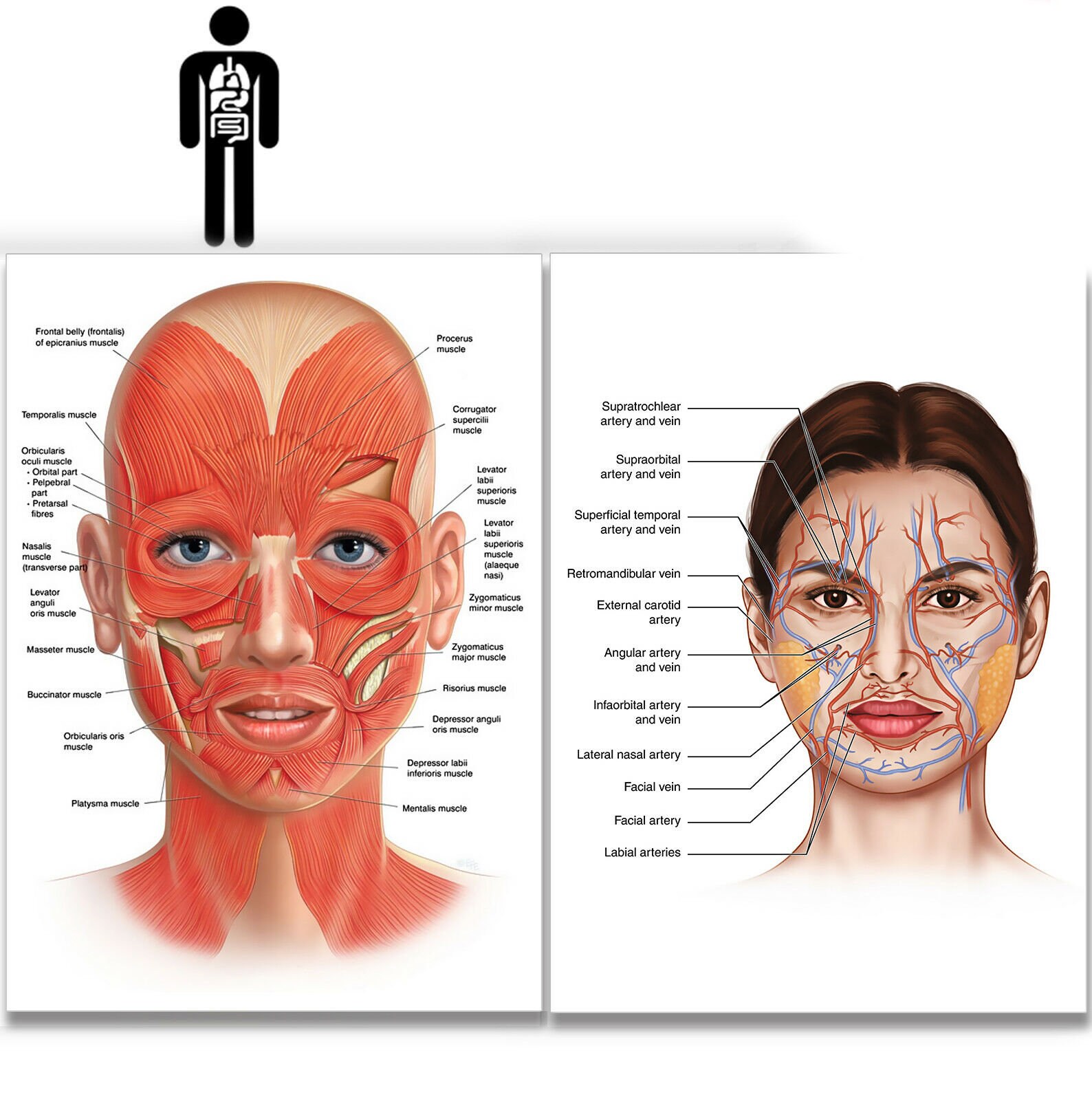
Facial Vein Retromandibular Vein Lymphatic Drainage of the Face The face possesses eyes, nose and mouth. It extends superiorly up to the hair line, inferiorly up to the chin and base of the mandible and on every side up to the auricle and is the front aspect of the head. The face and the scalp have the brow in common. Skin of the Face

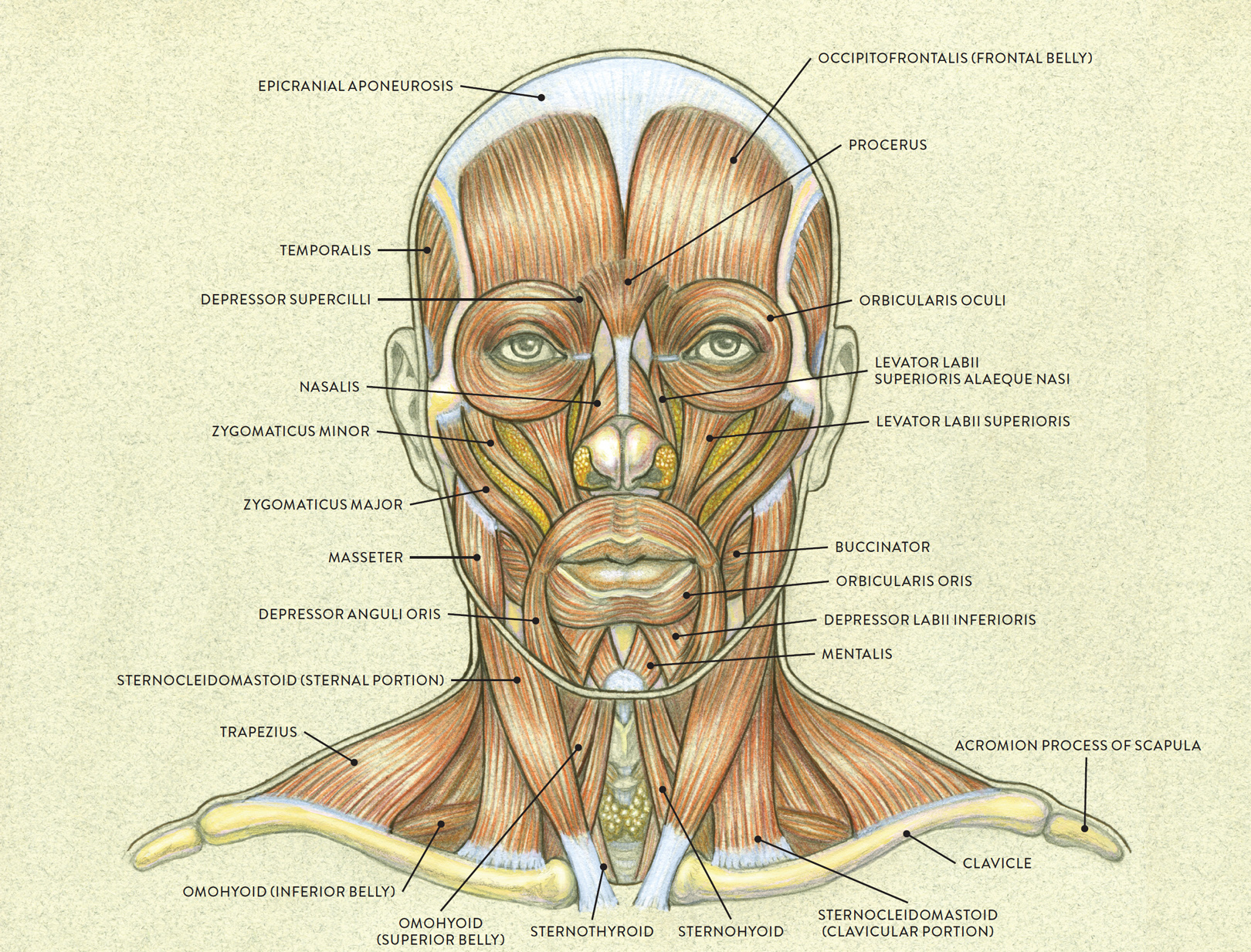
Anatomy and Physiology Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back
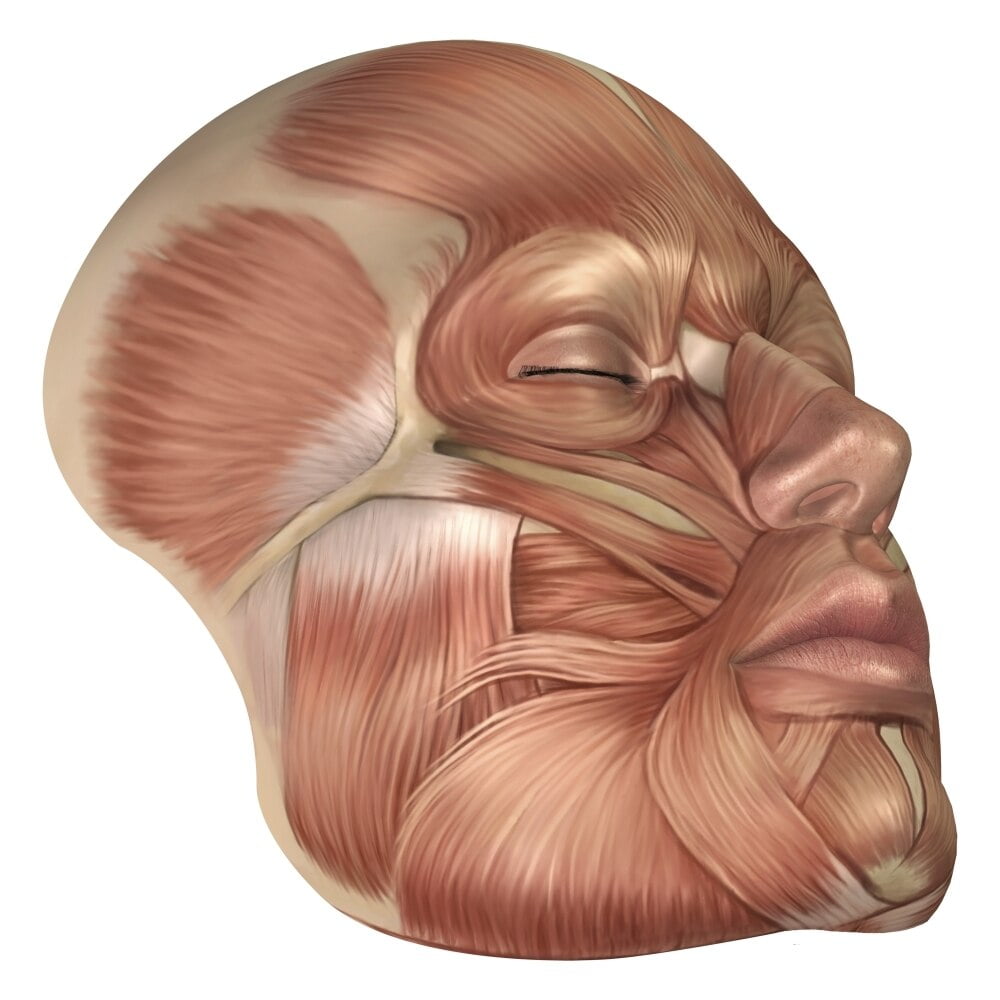
The human face possesses over two dozen individual muscles on each side - upwards of 30, depending on how they are counted. The facial muscles are striated muscles that link the skin of the face to the bone of the skull to perform important functions for daily life, including mastication and expression of emotion.

Know your face Do you know that you have 57 muscles in your face? Just like yoga tones and
Human face Author: Roberto Grujičić MD • Reviewer: Sophie Stewart Last reviewed: July 12, 2023 Reading time: 17 minutes Recommended video: Muscles of facial expression [12:24] Overview of the muscles responsible for facial expression. Muscles of facial expression Musculi faciales Synonyms: Facial muscles, Craniofacial muscles , show more.
Anatomy Of Face
face, front part of the head that, in vertebrates, houses the sense organs of vision and smell as well as the mouth and jaws. In humans it extends from the forehead to the chin. During the course of evolution from the prehuman Australopithecus to modern humans ( Homo sapiens ), the face became smaller in relation to the overall size of the head.

Pin on Facial Anatomy
A, Facial esthetic subunits. Forehead subunits: 1A, Central; 1B, Lateral; 1C, Eyebrow. Nasal subunits: 2A, Tip; 2B, Columellar; 2C, Dorsal; 2D, Right and left dorsal side wall; 2E, Right and left alar base; 2F, Right and left alar side wall. Periorbital subunits: 3A, Lower eyelid; 3B, Upper eyelid; 3C, Lateral canthal; 3D, Medial canthal.

Anatomy Of A Face Gallery Learn Human Anatomy Image Anatomy Anatomia musculos, Anatomia y
Basic Anatomy of the Face Angel Ganev 377K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 16K Share 260K views 3 years ago I show you the muscles and bones of the human face. ︎Support me on Patreon: /.
Anatomy of human face muscles Poster Print
In human face anatomy, all the features curve up and the ear moves up. Because the nose juts out, it oversteps its line (see figure) and the tip looks much closer to the mouth—if the face turns down enough, the nose will squarely overlap the mouth. Seen from this angle, the nose displays no details at all, just the wedge with a hint of wings.
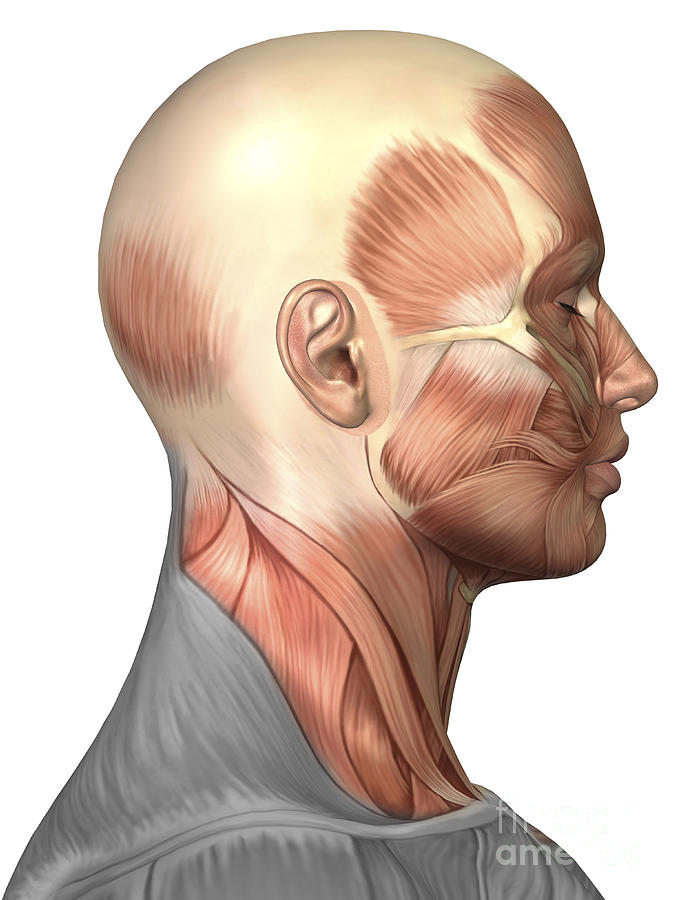
Anatomy Of Human Face Muscles, Side Digital Art by Stocktrek Images
In addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures: Muscles of mastication. Facial muscles. Salivary glands. Arteries. Nerves. In this page, we are going to focus on the head anatomy and those five less evident features and learn more about them.

FileLateral head anatomy.jpg Wikipedia
Development of the Face and Palate. The external human face develops between the 4 th and 6 th week of embryonic development. The development of the face is completed by the 6 th week. Between the 6 th and 8 th week, the palate begins to develop. Consequently, this causes a distinction between the nasal and oral cavities.

the facial anatomy is shown in this image, and shows the location of the facial area
ISSN 2534-5079. This head and neck anatomy atlas is an educational tool for studying the normal anatomy of the face based on a contrast enhanced multidetector computed tomography imaging (axial and coronal planes). Interactive labeled images allow a comprehensive study of the anatomical structures.