(PDF) Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes DOKUMEN.TIPS

(PDF) Descargar Measurement And Instrumentation Principles Alan S. Morris 3rd Edition
Part 1: Principles of Measurement 1 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEASUREMENT 3 1.1 Measurement units 3 1.2 Measurement system applications 6 1.3 Elements of a measurement system 8 1.4 Choosing appropriate measuring instruments 9 2 INSTRUMENT TYPES AND PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS 12 2.1 Review of instrument types 12 2.1.1 Active and passive instruments 12

Measurement and Instrumentation Edition 2 By Alan S. Morris and Reza Langari Elsevier
Free Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation notes pdf are very useful for Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation students in enhancing their preparation and improving their chances of success in Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation exam.

Ee2201 measurementandinstrumentationlecturenotes
February 16, 2023 by veer Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes: The notes provided in this series of lecture notes are for students to help create a better understanding of the subject. Students can use these notes to have a more thorough preparation for any upcoming exam.

Measurements and Instrumentation Lecture Notes (199) Manufactured Goods Physical Quantities
INTRODUCTION TO MEASURING Classification of InstrumentINSTRUMENTS: - deflecting, controlling and damping torques - -Ammeters and Voltmeters PMMC, moving iron, Electrostatic, induction type instruments - expression for the deflecting torque and control torque - Errors and compensations, extension of range ofinstruments. UNIT -II

EEE 353 Measurement and Instrumentation Course Teacher Md. Shamsul Arifin Assistant Professor
MEASUREMENT It is a process of comparing an unknown quantity with an accepted standard quantity. 1.1. ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENT &INSTRUMENTATION It is the branch of Electronics which deals with the study of measurement and variations of different parameters of various instruments. ⮚Why measurement of parameters and study of variations for

EEE (EN) ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION (KEE 302), UNIT1 LECTURE NOTES, Strictally
Course Objectives: The objectives of the course are to make the student learn about The basic principles of different types of electrical instruments for the Measurement of voltage, current, power factor, power and energy. The measurement of R, L, and C parameters using bridge circuits. The principles of magnetic measurements.

Introduction to Instrumentation and Measurements, 3rd Edition, Robert B. Northrop, 1138071900
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS 1.1 Definition of instruments An instrument is a device in which we can determine the magnitude or value of the quantity to be measured. The measuring quantity can be voltage, current, power and energy etc. Generally instruments are classified in to two categories. Instrument

Measurement and Instrumentation Edition 3 By Alan S. Morris and Reza Langari Elsevier
measurements system. UNIT - 3 CO3: To impart knowledge of mathematical modeling of the control system under different time domain. UNIT - 4 CO4: To analyze the stress and strain measurements and humidity measurements. UNIT - 5 CO5: To understand the measurements of Force, Torque and power and Elements of Control Systems.

(PDF) Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes DOKUMEN.TIPS
Lecture 20 : Resistance measurement with a Voltmeter and an Ammeter (Main) Download Verified; 21: Lecture 21 : Four-Terminal Resistance (Main) Download. Lecture 75 : Instrumentation Amplifier: Download Verified; 76: Lecture 76: Function generator: Download Verified; 77: Lecture 77: 555-Timer circuit: Download

Download Electrical Measurements And Instrumentation PDF Online 2020
Introduction Instrumentation: Where Knowledge and Reality Meet Instrumentation comprises scientific activities and technologies that are related to measurement. It is a link between physical, chemical and biological phenomena and their perception by humans.
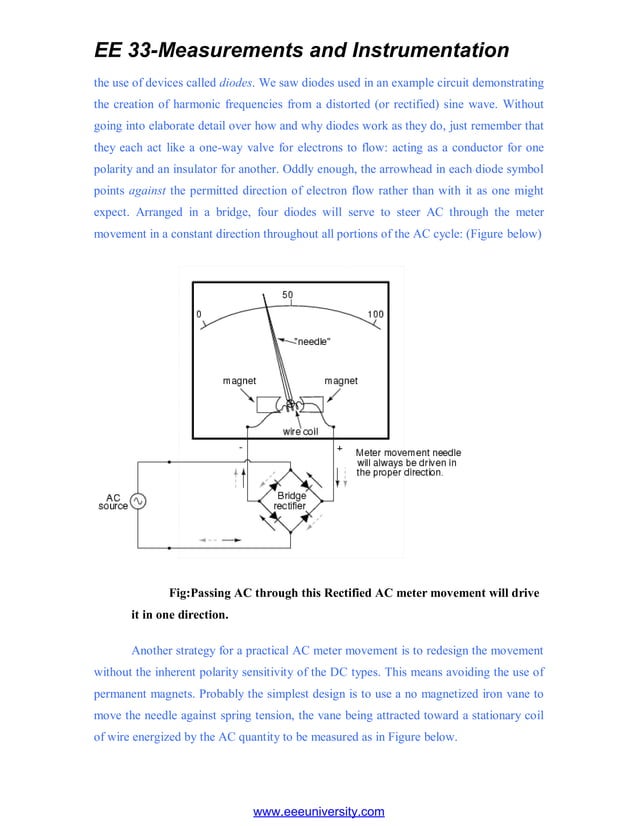
Ee2201 measurementandinstrumentationlecturenotes
Measurement & Instrumentation Lectures analytical or numerical results (e.g., from a finite element analysis) and verify that stress levels remain below safe limits for the material (e.g., below the yield strength). It is important to note that, because strain gages are finite in size, a measurement actually reflects an average of the strain over

ME41032 Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENTATION (Th. 3) Name of the course: Diploma in Electrical Engineering. t (4 h Semester) Notes Prepared by: RUBY SOREN.. ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION 1 = = in, is The . dc. (), ((or the the moving coil.

Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Lecture Notes Jntuk R16 ECE 42 Jntuk Materials
Contain an elastic elements that deforms under pressure and. creates a linear or angular displacement. The displacement is either displayed on a dial by means of. purely mechanical linkages or transformed to an electric signal. that can be displayed or recorder at will.

Unit 1 Measurement and Instrumentation LECTURE NOTES UNITI Signals and their representation
Measuring Instruments: Classification, Absolute and secondary instruments, indicating instruments, deflecting, control and damping torques, Ammeters and Voltmeters, PMMC, Moving Iron (MI) type, expression for the deflecting torque and control torque, extension of range using shunts and series resistance.

Measurements and Instrumentation Lecture Notes, Study Materials and Important questions
See Full PDFDownload PDF. 113 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Course Code: 13EE1114 L T P C 4 0 0 3 Pre requisites: Knowledge of Basic Network Analysis. Course Educational Objectives: To familiarize the students to various types of measuring instruments and their performance characteristics.

[PDF] Measurement and Instrumentation by Alan S. Morris eBook Perlego
Measurement - The process of determining the amount, degree, capacity by comparison (direct or indirect) with the accepted standards of the system units being used. Accuracy - The degree of exactness (closeness) of a measurement compared to the expected (desired) value.