Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology

Share 73+ eukaryotic cell sketch latest seven.edu.vn
Parts, Functions & Diagrams. Although there are differences among eukaryotes (creature that range from amoebae to elephant), overall, eukaryotic cells share many characteristics. Here's a breakdown. Article Summary: Animals, plants, fungi, protists, algae, and water & slime molds are eukaryotes, organisms composed of one or more nucleated cells.

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
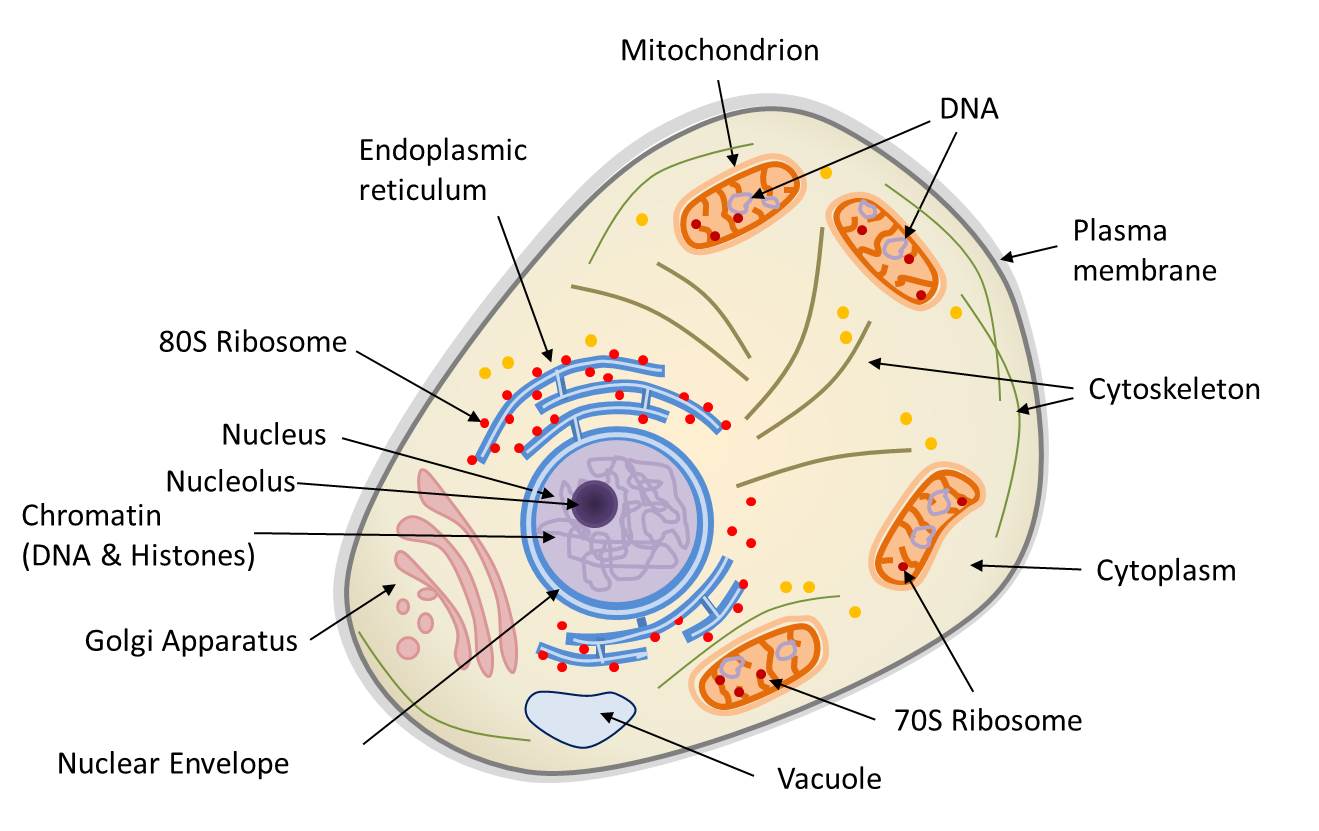
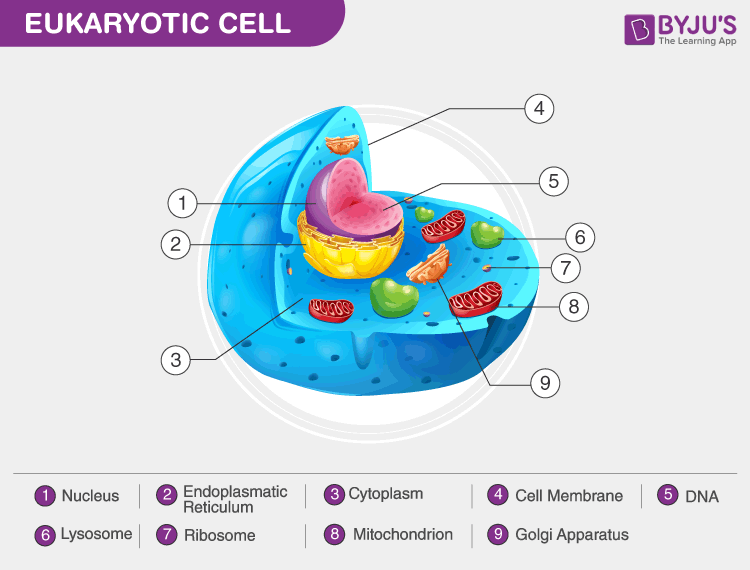
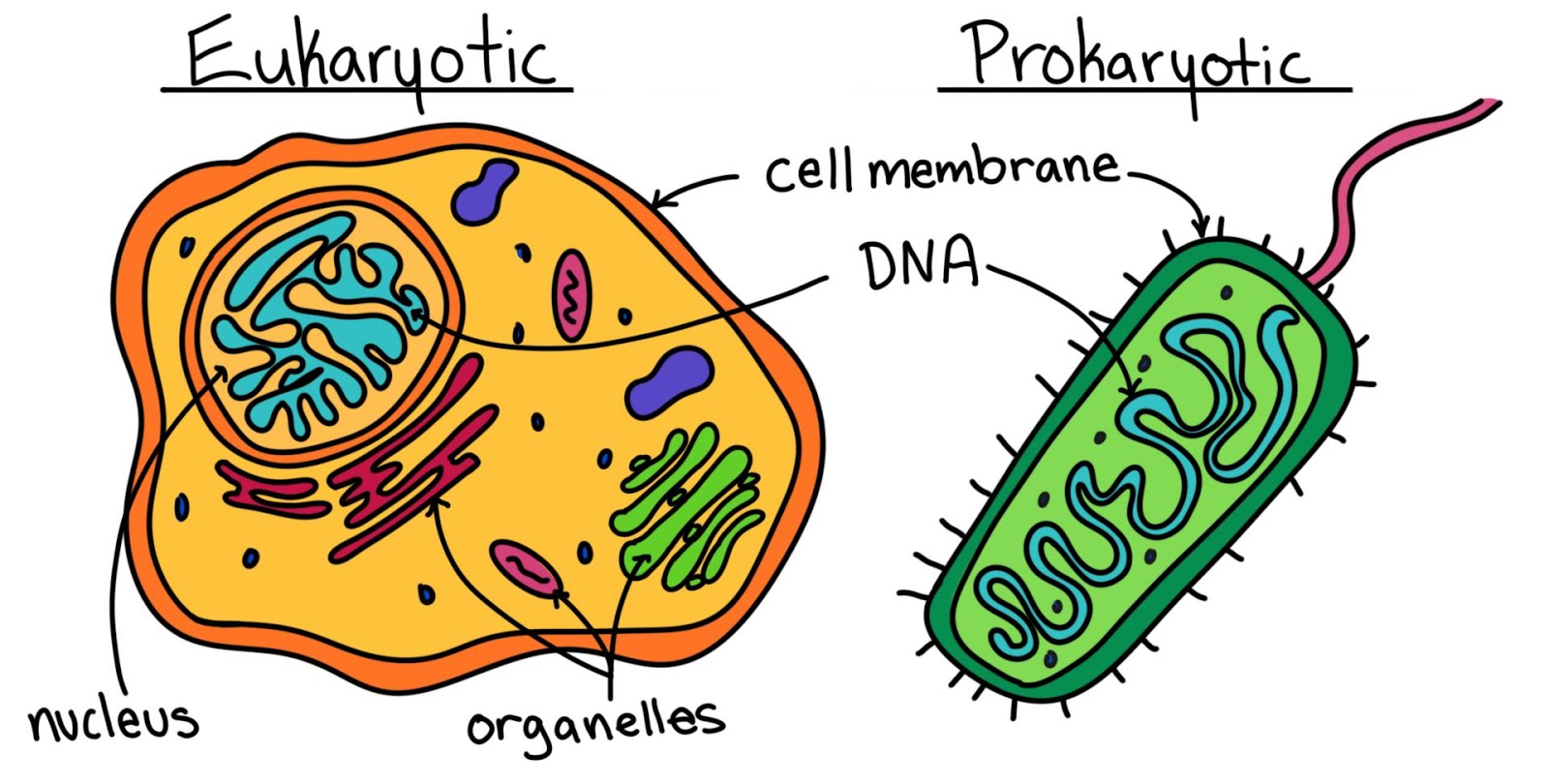
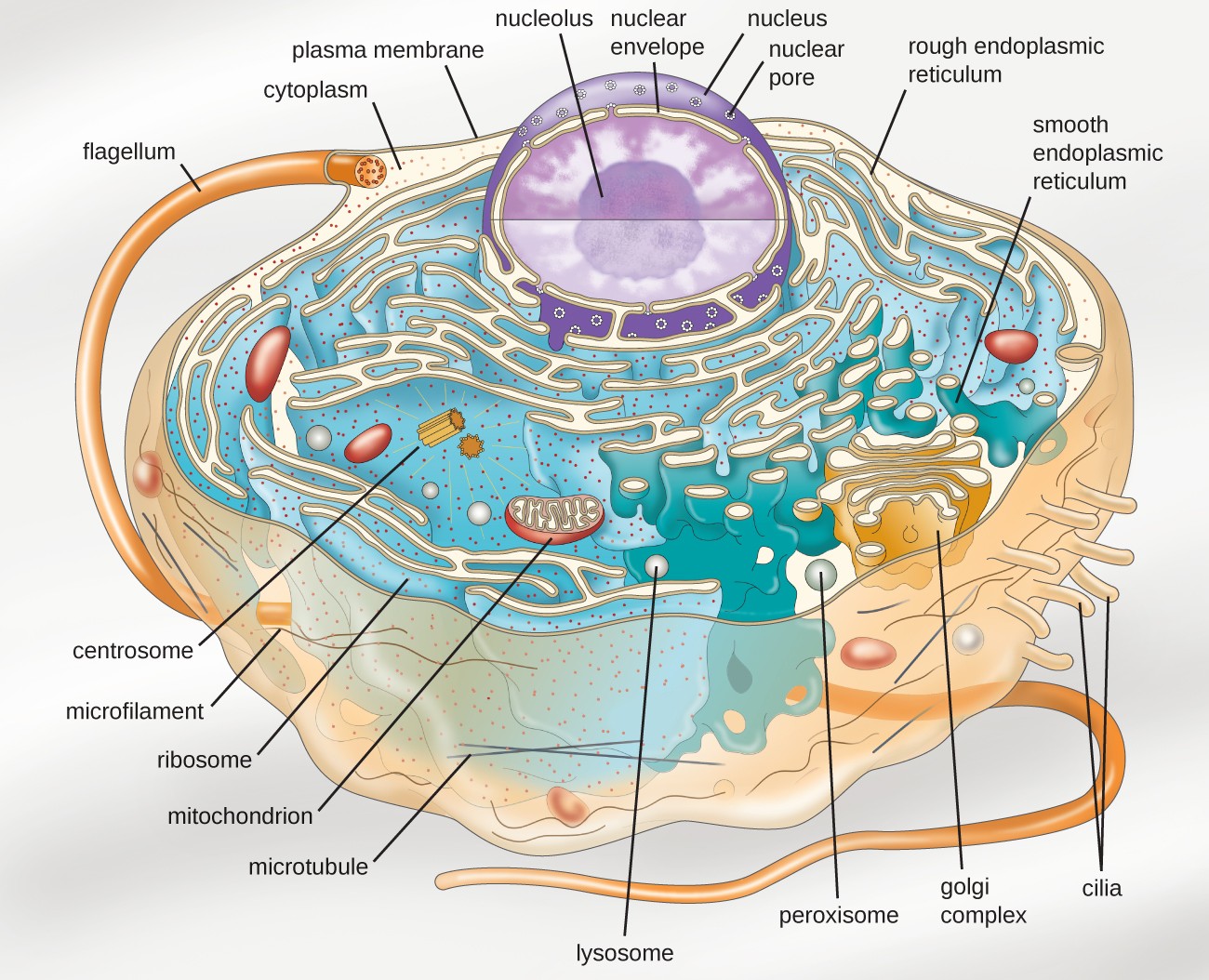
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus."
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others.
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples
An organelle (think of it as a cell's internal organ) is a membrane bound structure found within a cell. Just like cells have membranes to hold everything in, these mini-organs are also bound in a double layer of phospholipids to insulate their little compartments within the larger cells.
Bilingual Year 6 What are the different type of cells?
The Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the cell's entire region between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope (a structure we will discuss shortly). It is comprised of organelles suspended in the gel-like cytosol, the cytoskeleton, and various chemicals (Figure 4.8).Even though the cytoplasm consists of 70 to 80 percent water, it has a semi-solid consistency, which comes from the proteins.
31 Identify And Label Each Part Of This Eukaryotic Cell Labels For
What are the key features of eukaryotic cells? Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: A membrane-bound nucleus, a central cavity surrounded by membrane that houses the cell's genetic material. A number of membrane-bound organelles, compartments with specialized functions that float in the cytosol.

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.".

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
The Cell Wall. In Figure 3.3. 1 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls.

Eukaryotic cell structure diagrams Biological Science Picture
Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a Golgi apparatus (secretory device), an endoplasmic reticulum (a canal-like system of membranes within the cell), and lysosomes (digestive apparatus within many cell types).

Eukaryotic Cell Diagram
The structure of a eukaryotic cell is highly organized and compartmentalized, with various membrane-bound organelles and structures that perform specific functions. These structures are organelles that work together to maintain the cell's functions, including growth, energy production, and response to its environment..

Eukaryotic Cell Diagram
. Cells of animals, plants and fungi are called eukaryotic cells . Comparing cell types A group of organisms called Archaea are also prokaryotic. Next page Plant and animal cells Previous.

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Where are they Found Eukaryotic cells are located in plants, animals including humans, fungi, and protozoa. They are together classified under the kingdom Eukaryota. How did Eukaryotic Cells Evolve The first eukaryotic cells probably evolved about 2 billion years ago. The endosymbiotic theory explains their evolution.
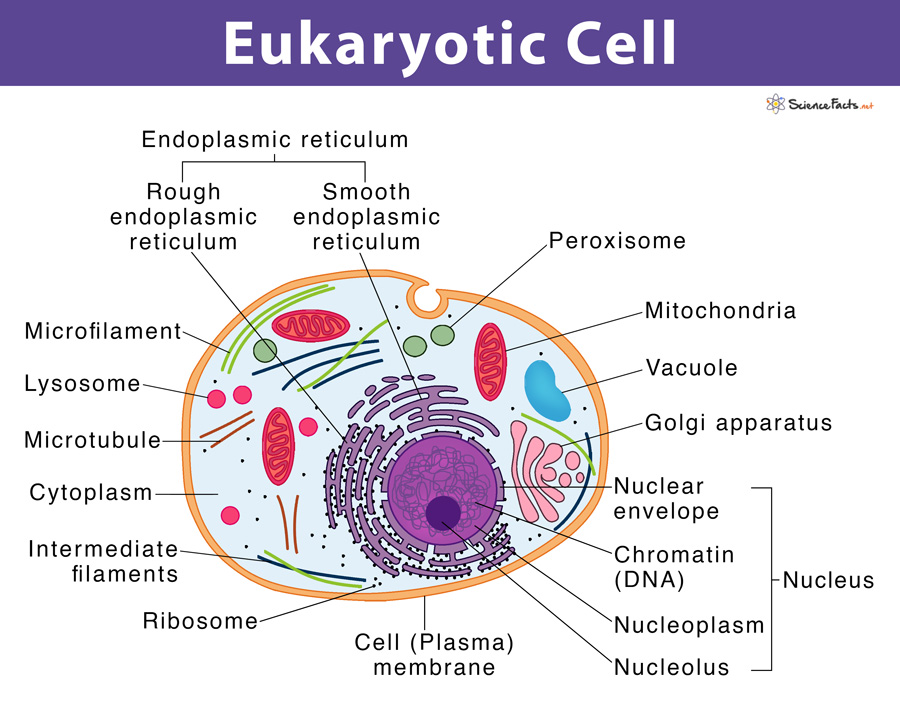
Eukaryotic Cells Definition Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Parts Structure
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.

Eukaryotic Cells The Cell MCAT Biology Review
Overview of the cell and its contents. Plasma membrane Plasmalemma 1/5 Synonyms: Cell membrane, Membrana cellularis The cell is the smallest functional unit within a living organism, which can function independently. It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce.

Eukaryotic cell 951 plays Quizizz
The Cytoplasm In cell biology, each eukaryotic cell is separated into two categories: the nucleus, which we just described above, and the cytoplasm, which is, well, everything else.

2.2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Biology LibreTexts
Diagram Cell Cycle Examples What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.