Diagrams of a Microscope 101 Diagrams
Guide to understand microscope parts, names, functions & diagram
There are 1000 millimeters (mm) in one meter. 1 mm = 10 -3 meter. There are 1000 micrometers (microns, or µm) in one millimeter. 1 µm = 10 -6 meter. There are 1000 nanometers in one micrometer. 1 nm = 10 -9 meter. Figure 1: Resolving Power of Microscopes. The microscope is one of the microbiologist's greatest tools.
Microscopes 7th Grade Science
Parts of the Microscope (Labeled Diagrams) By Editorial Board December 14, 2022 The microscope is one of the must-have laboratory tools because of its ability to observe minute objects, usually living organisms that cannot be seen by the naked eyes. It is categorized into two: simple and compound microscopes.
How to Use a Microscope
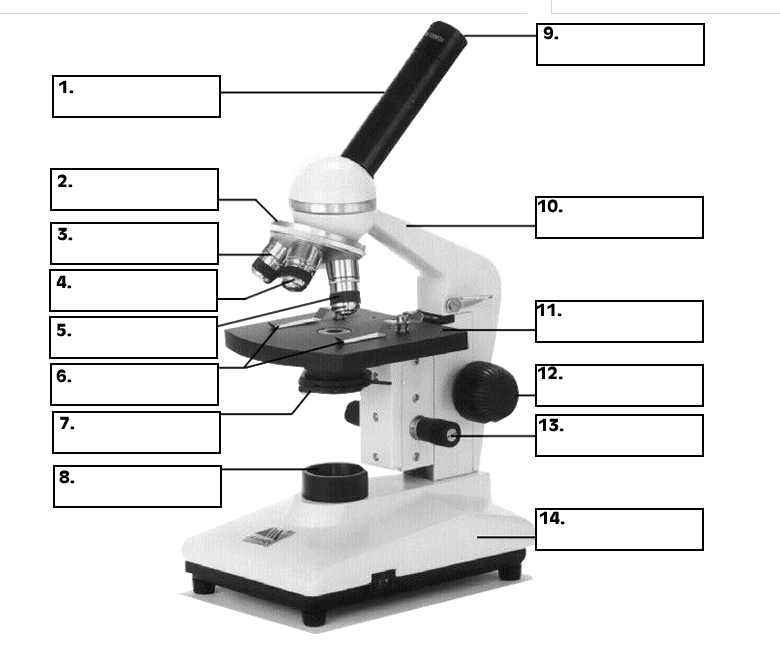
1. Eyepiece Lens and Eyepiece Tube 2. Objective Lens 3. Tube 4. Base 5.

Light Microscope Main Parts Of Light Microscope Biology —
Parts of a Compound Microscope Each part of the compound microscope serves its own unique function, with each being important to the function of the scope as a whole. The individual parts of a compound microscope can vary heavily depending on the configuration & applications that the scope is being used for. Common compound microscope parts include: Compound Microscope Definitions for.

Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
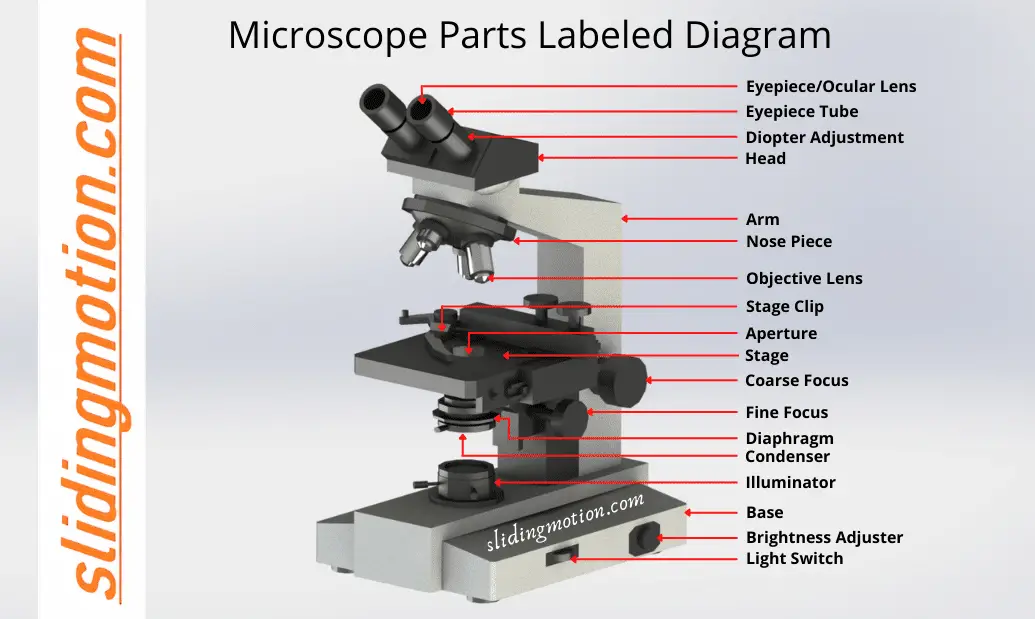
16 Essential Microscope Parts: Names, Functions & Labeled Diagram by Swap Table of Contents Overview of Microscope Anatomy Microscope Parts Labeled Diagram Parts of a Microscope Microscope Parts and Functions Head Base Arm Eyepiece Eyepiece tube Objective lenses Nose Piece The adjustment knobs Stage Aperture Microscopic Illuminator Condenser

Diagrams of Microscope 101 Diagrams
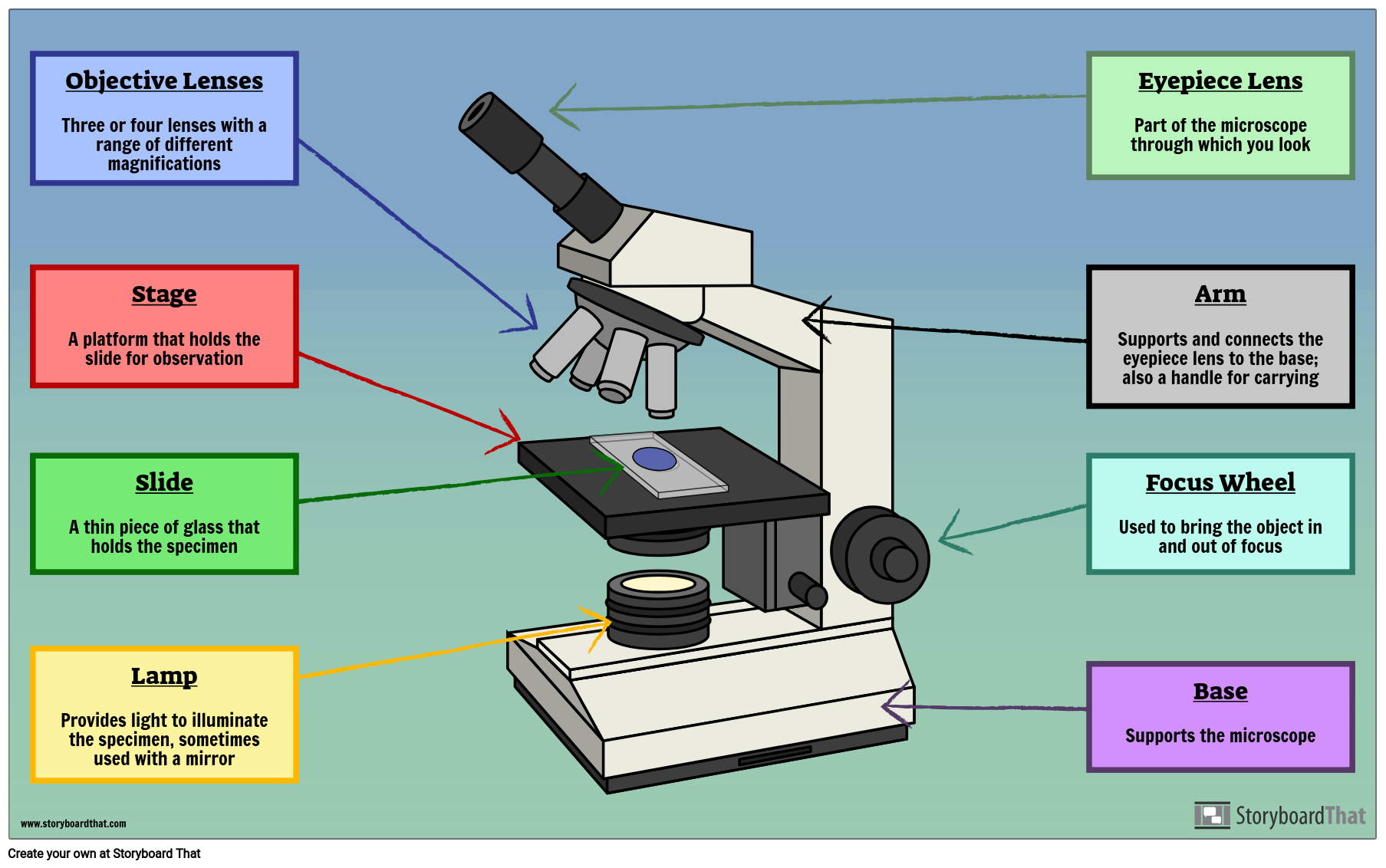
The main parts include the following: Fig: Parts of the microscope Labeled diagram Table of Contents Structural parts of a microscope: Optical parts of a microscope The Eyepiece The Eyepiece tube The objective lenses The focus knobs Stage The light source (Illuminator) Condenser The condenser focus knob The diaphragm

301 Moved Permanently
Parts of a Microscope and their Functions. The microscope comprises three main structural components: the head, the base, and the arm. HEAD: Also known as the body, the microscope's head houses the optical components in the upper portion. BASE- It serves as a support for microscopes. Illuminators for microscopic work are also included.

The Free Information Society Optical Microscope Diagram
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, microscopes have revolutionized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable. Derived from Greek words "mikrós" meaning "small" and "skópéō" meaning "look at". Table of Contents
36 Label Parts Of The Microscope Labels 2021
The hand magnifying glass can magnify about 3 to 20×. Single-lensed simple microscopes can magnify up to 300×—and are capable of revealing bacteria —while compound microscopes can magnify up to 2,000×. A simple microscope can resolve below 1 micrometre (μm; one millionth of a metre); a compound microscope can resolve down to about 0.2 μm.
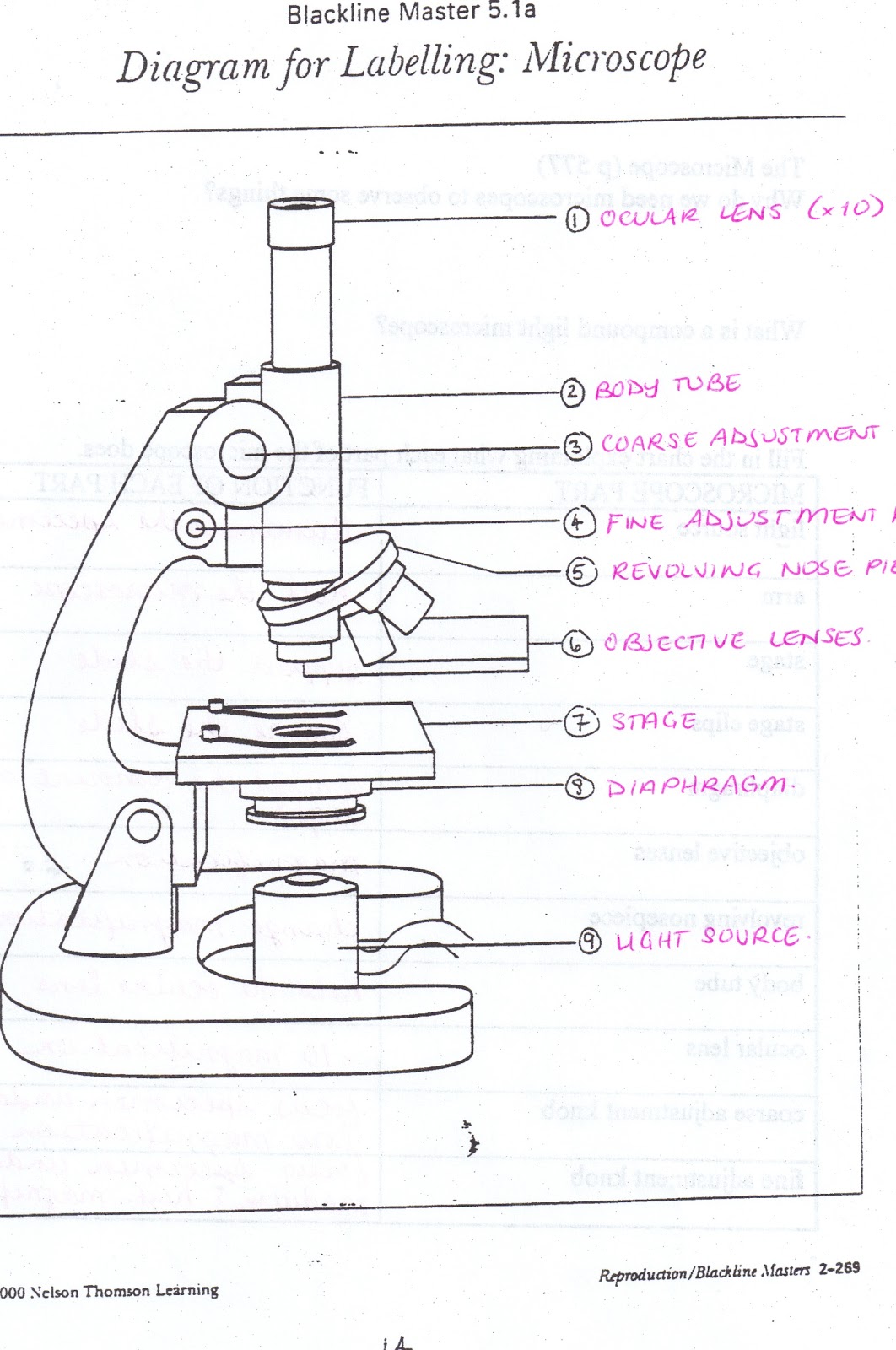
All Saints Online Diagram for Labelling Microscope
Explore the different parts of a microscope using a diagram, including the microscope lens, eyepiece, and stage. Updated: 10/13/2022 What is a Microscope? A microscope is a scientific.

Microscope Diagram Labeled, Unlabeled and Blank Parts of a Microscope
The microscope illustrated in Figure 5 below was manufactured by Hugh Powell and Peter Lealand around 1850. The tripod base provided a sturdy support for the microscope, which many people consider the most advanced of its period. Parts of a Powell and Leland Microscope Diagram
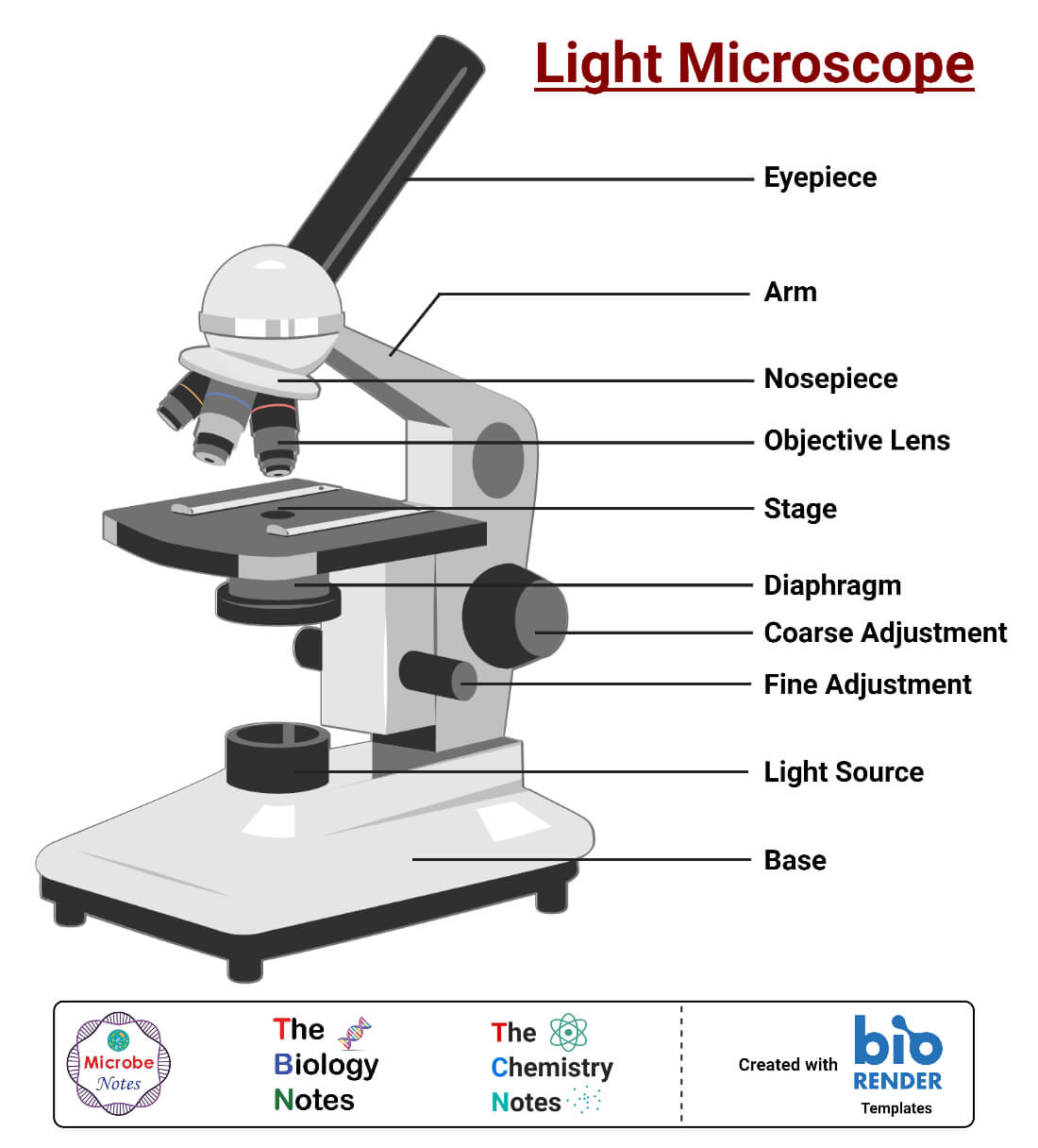
🎉 Main components of a light microscope. Parts of a microscope with
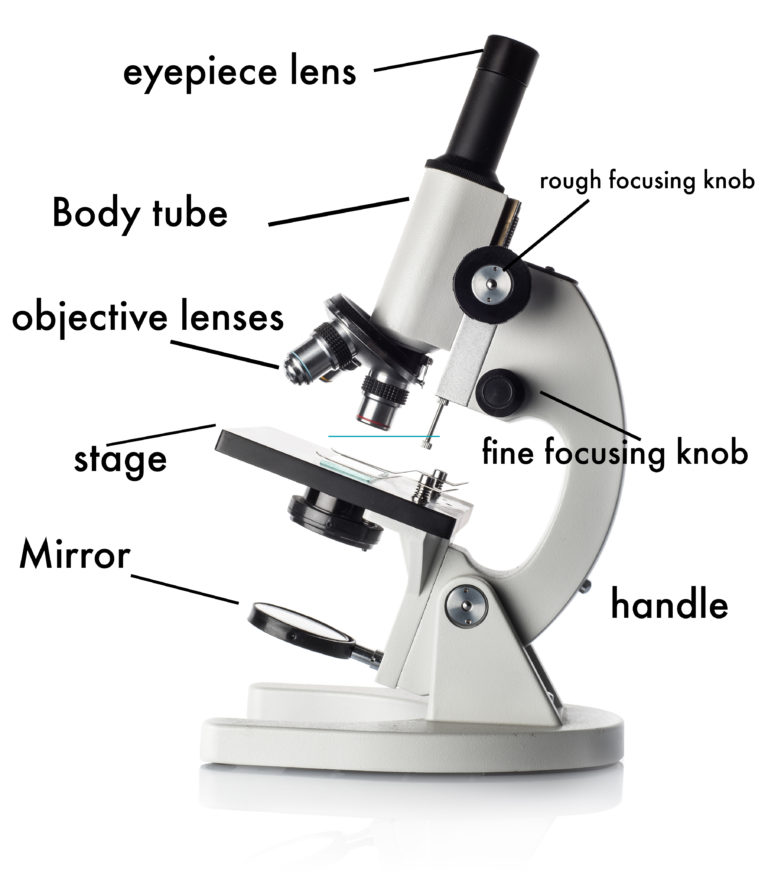
Tube: Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Arm: Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Base: The bottom of the microscope, used for support. Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom.
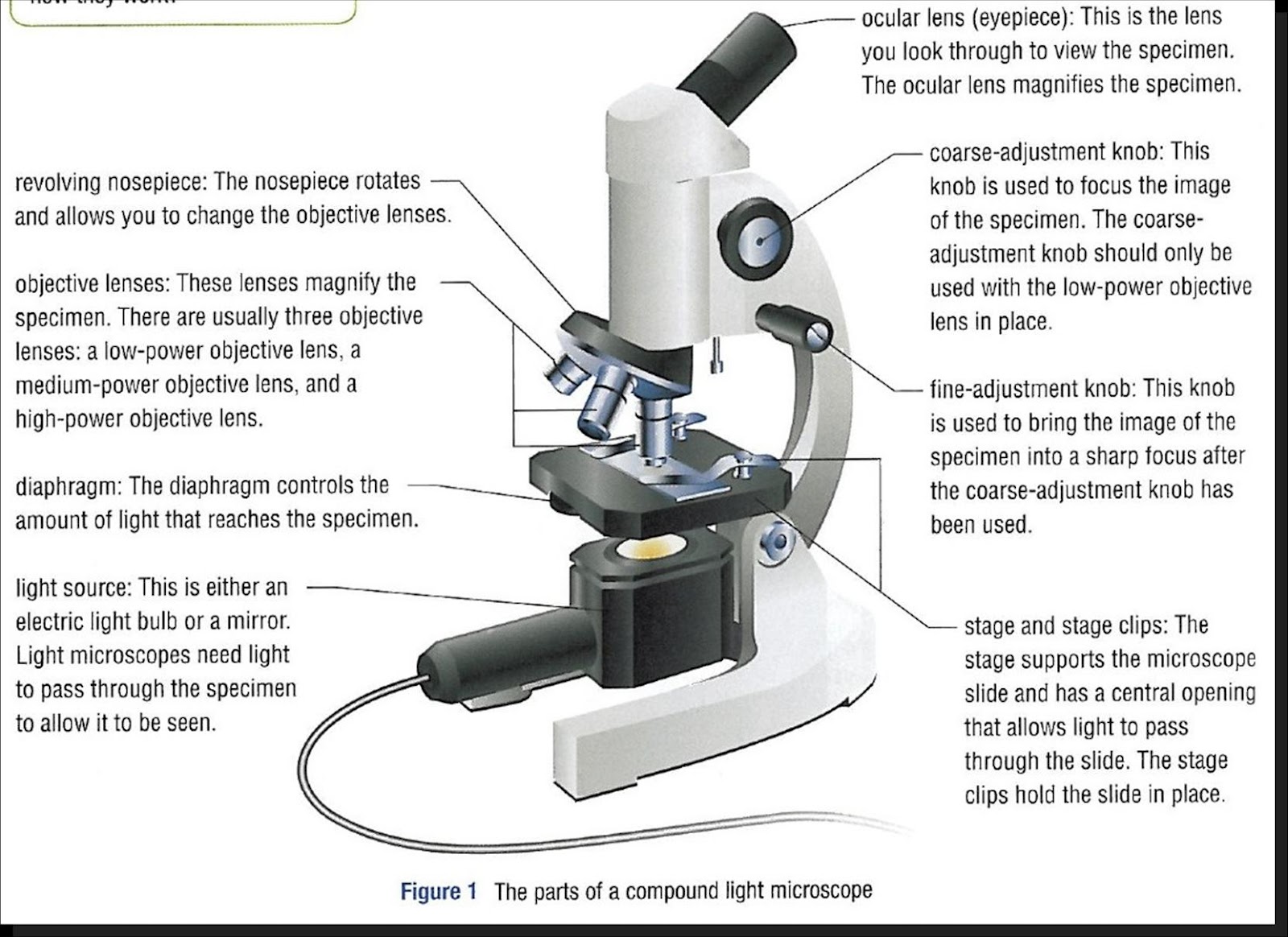
Parts Parts And Functions Of A Microscope
There are two major types of electron microscopy. In scanning electron microscopy ( SEM ), a beam of electrons moves back and forth across the surface of a cell or tissue, creating a detailed image of the 3D surface. This type of microscopy was used to take the image of the Salmonella bacteria shown at right, above.

Diagrams of Microscope 101 Diagrams
The 16 core parts of a compound microscope are: Head (Body) Arm Base Eyepiece Eyepiece tube Objective lenses Revolving Nosepiece (Turret) Rack stop Coarse adjustment knobs Fine adjustment knobs Stage Stage clips Aperture Illuminator Condenser Diaphragm Video: Parts of a compound Microscope with Diagram Explained

Microscope Diagram to Print 101 Diagrams
Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen. Condenser: Gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed. Base: The base supports the microscope and it's where illuminator is located. How Does a Compound Microscope Work?

Microscope Parts Sketch at Explore collection of
The field diaphragm control is located around the lens located in the base. Hinge Screw -This screw fixes the arm to the base and allow for the tilting of the arm. Stage Clips - They hold the slide firmly onto the stage. On/OFF Switch - This switch on the base of the microscope turns the illuminator off and on.